Dev Ops Hacks
Observe an algorithm using parallel computing in Python Code. Monitor processes on host.
Kasm Hacks:
Virtual desktops allow users to access a complete operating system and applications hosted on a remote server from any device with an internet connection. KASM is a security solution that ensures the virtual desktop environment is protected from malware and other cyber threats. In the AP CSP environment, virtual desktops can provide students with a consistent and secure computing experience, regardless of the hardware and software they have access to at home or school.

- Diagram of pros and cons of DuckDNS
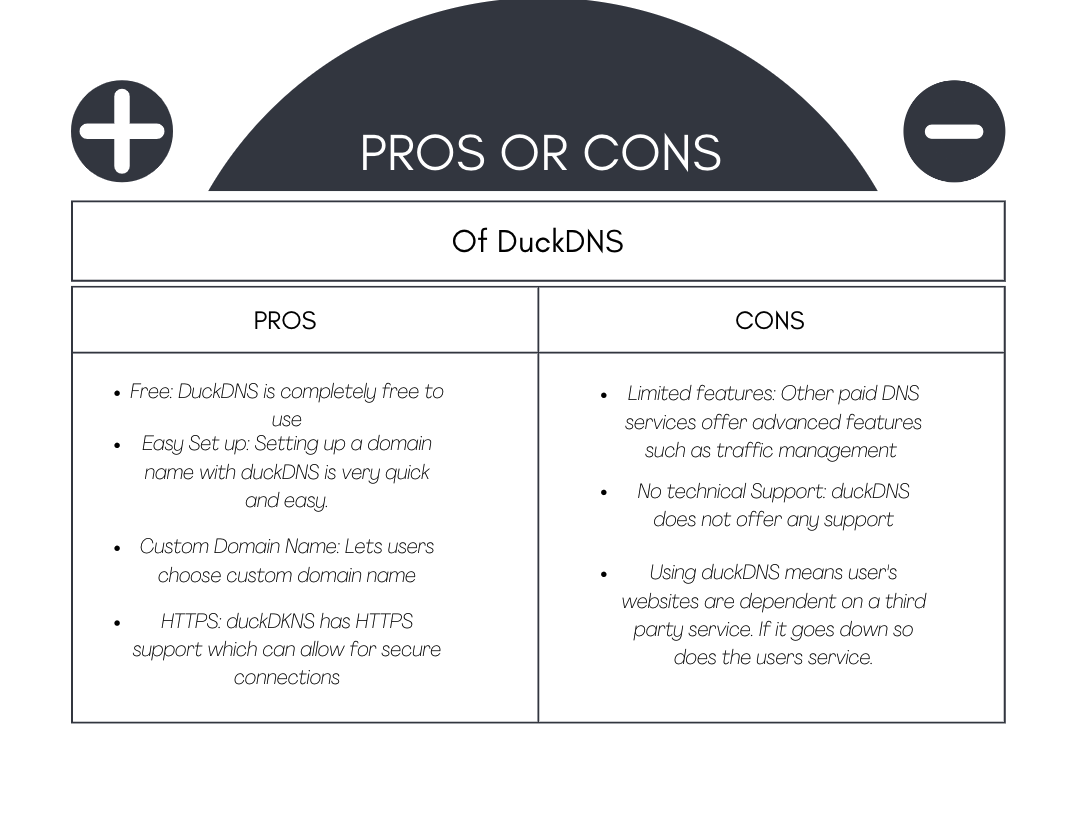
- Reflection DNS is used to translate human-readable domain names to machine-readable IP addresses. DuckDNS is a free dynamic DNS service that assigns a domain name to a home network's public IP address. It is useful for projects that require remote access and is easy to set up by creating an account, running the client, and configuring the router.
- One outdated Nginx/Docker functionality that may need to be addressed is the use of the deprecated "docker run" command, which has been replaced by "docker container run". Additionally, outdated Nginx/Docker configurations may include insecure SSL protocols and ciphers, which can compromise security and should be updated to use modern and secure options.
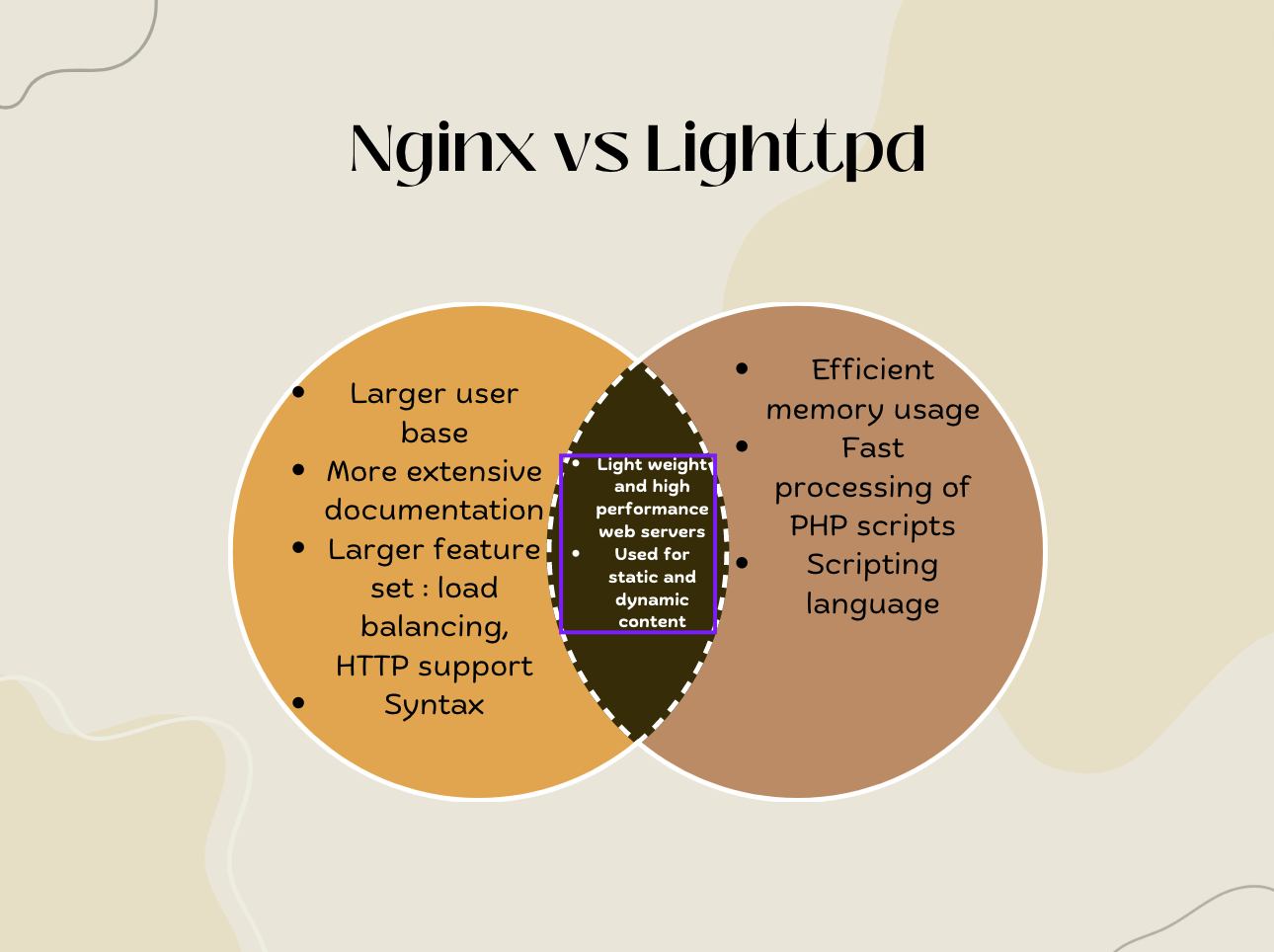
- Venn Diagram
import getpass, sys
# method to display question and get user's answers
def question_with_response(prompt, qCount):
print("Question " + str(qCount) + " : " + prompt)
msg = input()
return msg
# dictionary to hold questions and answers as key : value pairs
questionsDict = {"What does Domain Name Server represent?": "DNS",
"What does this Represent: Amazon Web Services, which is a cloud computing platform provided by Amazon.": "AWS",
"What is the first Step to setting up an AWS Server? 1: Connecting to a Ubuntu EC2 Instance, 2: Start updating the system, 3: Clone the repository which one wishes to deploy, 4: Run the command: main.py to start the project": "1",
"What is the third Step to setting up an AWS Server? 1: Connecting to a Ubuntu EC2 Instance, 2: Start updating the system, 3: Clone the repository which one wishes to deploy, 4: Run the command: main.py to start the project": "3",
"What is the fourth Step to setting up an AWS Server? 1: Connecting to a Ubuntu EC2 Instance, 2: Start updating the system, 3: Clone the repository which one wishes to deploy, 4: Run the command: main.py to start the project": ".4",
"What is the second Step to setting up an AWS Server? 1: Connecting to a Ubuntu EC2 Instance, 2: Start updating the system, 3: Clone the repository which one wishes to deploy, 4: Run the command: main.py to start the project": "2",
"What files are you supposed to edit after finishing the first steps of setting up the server and cloning it within the AWS Server? 1: Edit the docker files and docker.yml, 2: Edit the main.py file to change the characteristcs.": "1",
"What is the first step to setting up a DuckDNS Server? 1: Sign in with your DuckDNS account using Github, 2: Configure current ip to the IP address that you want to access and click update ip button , 3: Create the subdomain, 4: Access site by typing in subdomain.duckdns.org": "1",
"What is the second step to setting up a DuckDNS Server? 1: Sign in with your DuckDNS account using Github, 2: Configure current ip to the IP address that you want to access and click update ip button , 3: Create the subdomain, 4: Access site by typing in subdomain.duckdns.org": "3",
"What is the third step to setting up a DuckDNS Server? 1: Sign in with your DuckDNS account using Github, 2: Configure current ip to the IP address that you want to access and click update ip button , 3: Create the subdomain, 4: Access site by typing in subdomain.duckdns.org": "2",
"What is the fourth step to setting up a DuckDNS Server? 1: Sign in with your DuckDNS account using Github, 2: Configure current ip to the IP address that you want to access and click update ip button , 3: Create the subdomain, 4: Access site by typing in subdomain.duckdns.org": "4"
}
# number of questions as length of the dictionary
questions = len(questionsDict)
# set correct to 0
correct = 0
print('Hello, ' + getpass.getuser() + " running " + sys.executable)
print("You will be asked " + str(questions) + " questions.")
print("Are you ready to take a test! Press Enter key to begin. Best of luck :)")
input()
questionCount = 0
# iterate over list of keys from the dictionary. pass dictionary key as question to the question_with_response function
for key in questionsDict:
questionCount += 1
rsp = question_with_response(key, questionCount)
# compare the value from the dictionary to the user's input
if rsp.lower() == questionsDict[key].lower():
print(rsp + " is correct! Good Job!")
correct += 1
else:
print(rsp + " is incorrect! Better Luck next time.")
# print final score
print(getpass.getuser() + " you scored " + str(correct) +"/" + str(questions))
# calculate percentage
page = correct/questions * 100
# print percentage
print("Total Percentage: " + str (format(page,".2f")) + "%")
- I couldn't get the sudo certbot command to work
- OpenSSL and LibreSSL are both open-source cryptographic libraries that offer similar security features such as support for a wide range of cryptographic algorithms and functions for secure random number generation, SSL/TLS protocol implementation, and X.509 certificate handling. One main difference is that LibreSSL aims to modernize OpenSSL by removing deprecated features and adding new security features. Both have had recent high-severity vulnerabilities, but patches were quickly released to fix them.